Most Canadians are familiar with CPP, which provides retirement, disability, survivor, and death benefits for individuals that have been employed in Canada.1 CPP is funded by mandatory annual contributions by employees, employers and self-employed individuals based on their CPP pensionable earnings, which typically include salary, wages or other remuneration, commissions, bonuses, most taxable benefits, and tips/gratuities.
Responding to concerns that Canadians may not be financially prepared for retirement, the federal government has rolled out a series of enhancements to the CPP program over the last few years.
Enhancements to CPP
The first phase of CPP enhancements was implemented from 2019 to 2023, during which time the CPP contribution rate was increased incrementally from 4.95% to 5.95%. The pre-enhancement contribution rate of 4.95% is referred to as the “CPP base” rate, and the 1% increase is referred to as the “CPP enhancement” rate.
The second phase of CPP enhancements, commonly referred to as “CPP2”, takes effect in 2024. CPP2 introduces a second level of CPP contributions that are applied to an additional tier of eligible income over the YMPE, up to the second earnings ceiling, or YAMPE. For 2024, the YAMPE will be $73,200, approximately 7% above the YMPE. It will increase to approximately 14% above the YMPE in 2025 and thereafter.
Other than the annual YMPE and YAMPE figures being adjusted annually for inflation, no further CPP enhancements are anticipated after 2025.
To understand the enhancements, here are some key CPP definitions:
Annual basic exemption: The annual amount of earnings by employees or self-employed individuals for which CPP contributions are not required. For 2024, the basic exemption amount is $3,500.
Contribution rate: The percentage of an employee’s pensionable earnings they contribute to the CPP. Self-employed individuals contribute double, or effectively both the employee and employer-matched contributions. For 2024, the employee contribution rate is 5.95%, and the self-employed rate is 11.90%.
CPP2 contribution rate: If an employee/selfemployed individual’s income is greater than the YMPE (see below), the CPP contribution rate will be 4.00% for employees and their employers, or 8.00% for self-employed individuals.
Year’s maximum pensionable earnings (YMPE): The maximum pensionable earnings for which employee and employer CPP contributions are required in a year. For 2024, the YMPE is $68,500. The YMPE is now commonly referred to as the “first earnings ceiling.”
Year’s additional maximum pensionable earnings (YAMPE): New for 2024, this additional tier of maximum pensionable earnings will be set at $73,200. The YAMPE is referred to as the “second earnings ceiling.”
Maximum contributory earnings: The maximum earnings to which the contribution rate is applied. It is the YMPE less the basic exemption amount. For 2024, the maximum contributory earnings are $65,000 ($68,500 – $3,500).
How are CPP contributions reported for income tax purposes?
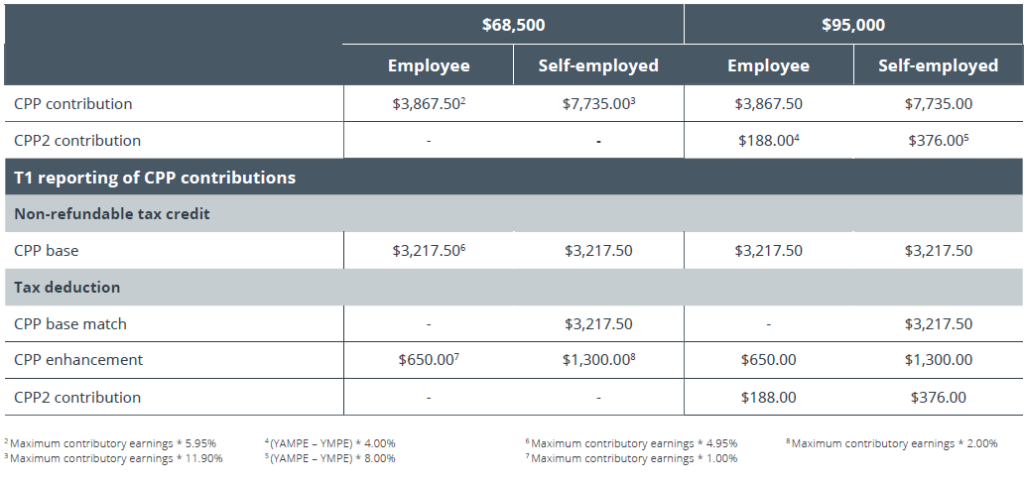
For 2024, let’s consider the following scenarios for Mike, to outline CPP and CPP2 considerations:
Employees and self-employed individuals are entitled to a non-refundable tax credit for their CPP base contributions. CPP base match amounts for self-employed individuals, CPP enhancement contributions and CPP2 contributions are claimed as tax deductions on individuals’ annual Income Tax and Benefit Return (T1).
A tax deduction reduces income subject to taxes. A tax credit reduces income taxes owing. The appropriate CPP contributions generate a non-refundable federal tax credit of 15% (plus applicable provincial/territorial credit).
Additional Thoughts
The introduction of CPP2 will result in higher CPP contributions for some workers, having a maximum impact of $188 on employees and $376 on selfemployed individuals with income at or above the YAMPE level of $73,200 for 2024. The CPP enhancements introduced since 2019 will ultimately have a positive effect, however, for Canadians entitled to receive the following CPP benefits:
CPP retirement pension
- CPP post-retirement benefit
- CPP disability pension
- CPP survivor’s pension
More information about the CPP enhancements is available from the following resources:
1 Except in the province of Quebec, which administers its own plan called the Quebec Pension Plan (QPP)