The Future Looks Bright, Indeed!
It has been said that millennials — those born from 1980 to 1994 — were the first generation worse off than their parents financially. Skyrocketing housing prices, a higher cost of education and a challenging economy, among others, were to blame. And while things didn’t look so great for the millennials a decade ago, recent studies suggest a different story.
Millennials have caught up to previous generations and are expected to thrive. As they begin turning 43 this year — the average age when we “stop feeling young” — their household income is higher than previous generations at the same age: $9,000 more than the median GenX (1965 to 1979) household income and $10,000 more than the Boomers (1946 to 1964), in 2019 dollars.1 While these are U.S. figures, a recent Canadian study paints a similar picture of a more highly-educated younger population, which has contributed to their success.2
The future may look bright, after all. As they enter their peak earning years, millennials will continue to support the economy, including in investing. Today, millennials hold just 2.3 percent of total U.S. stock and funds,3 a trend that is likely to change as greater wealth is accumulated and assets are invested to meet their future goals.
This narrative isn’t unique; every generation has had its challenges. GenX entered the job market during a recession and was subjected to “dire predictions” about their economic futures. This was just 30 years ago, in 1993, when Joe Carter’s home run would win the Blue Jays their second consecutive World Series. It was a challenging economic period. Canada was emerging from a recession described as “the deepest since the Great Depression.” Unemployment had soared to over 11 percent after interest rates were aggressively raised to fight inflation.4 Then-Prime Minister Mulroney would end up resigning after his popularity fell from imposing the then-seven percent GST two years earlier. Canada’s future economic prospects looked bleak for the near term: An editorial to start 1995 referred to “Bankrupt Canada” as “an honourary member of the Third World.”5 Yet, the years that would follow would be in significant contrast. Canada would post consistent budget surpluses to end the 1990s (a concept foreign to many governments today), and GDP growth would surge.
Indeed, time can be the great equalizer. Economies are cyclical, and the rebound of the 1990s — and the millennials — should remind us not to get too caught up in the present. This, too, may be true in investing. Consider that an investment of $100,000 in the S&P/TSX Composite Index during this seemingly bleak period 30 years ago would have grown to $628,273 today, or $1,318,767 with dividends
reinvested.6 However, participating in this growth required having confidence in the prospect of better days ahead.
While the summer is the season for well-deserved downtime, make sure that your assets are working hard for you — money needs no vacation. Keep time on your side. Continue looking forward and positioning your assets for the brighter days ahead!
[1] www.wsj.com/articles/millennials-turning-40-feeling-old-1df2c83b; www.theatlantic.com/magazine/archive/2023/05/millennial-generation-financial-issues-income-homeowners/673485/; [2] www.desjardins.com/content/dam/pdf/en/personal/savings-investment/economic-studies/canadian-youth-education-employment-17-april-2023.pdf; [3] U.S. Federal Reserve, “Distribution of Household Wealth in the U.S. Since 1989,” at Q4 2022; [4] www.bankofcanada.ca/2001/01/canada-economic-future-what-have-we-learned/; [5] www.reuters.com/article/us-crisis-timeline-idUSTRE7AK0FF20111121; 6. S&P/TSX Composite and Total Return Indices, 01/29/93 to 1/31/23 (3,305.47 to 20,767.40; 6,124.83 to 80,772.20).
PLANNING AHEAD
Has the Hot Housing Market Changed Your Outlook?

After a slowdown that lasted almost a year, largely blamed on rising interest rates, the spring brought a revival to Canada’s housing market. Supply fell to a 20-year low to start the residential sales season, which helped to push prices higher. Will the rebound continue? For many investors, the significant gains in housing prices over the past decade have changed the way we plan for retirement. Here are two challenges:
1. Relying on home equity in retirement. Sometimes a home’s value may be viewed as a potential source of retirement income, but we often suggest exercising caution for a variety of reasons. While your home equity certainly counts as part of your net worth, the main way it can be turned into investable capital is through its sale. Of course, loans such as a home equity line of credit (HELOC) grew in popularity when interest rates were at historical lows, but the significant cost of interest payments as rates have risen should not be overlooked. For those who wish to sell their homes, one pitfall is failing to consider the “true” value of a home. Future real estate values are never guaranteed, and there are often unanticipated costs associated with a sale, such as renovations or maintenance. At the end of the day, you still need a place to live, and this may be more costly than anticipated. Still, others eventually find that selling a lifelong home ends up being too emotionally difficult. There are exceptions: some choose to become renters; others retire abroad to more affordable destinations. However, even in these circumstances, planning for contingencies is important — you may be unable to find a suitable long-term rental property, or perhaps you will eventually decide to move back, such as to access Canada’s healthcare system.
2. Supporting future generations to buy a home. With the cost of home ownership becoming increasingly out of reach, many have been assisting children/grandchildren. By some accounts, the average gift in the two most expensive markets, Toronto and Vancouver, ranged from $130,000 to $180,000, with some gifts in excess of $300,000.1 Given these substantial amounts, it is important to carefully factor in how financial support may affect the gifter’s own retirement plans — a recent survey suggests that 34 percent of parents are using their retirement savings to help adult kids.2
Consider also the different ways to provide support, such as purchasing a property in your name, gifting cash or lending funds to the child. Each comes with various tax and family law issues. For example, if the home is not designated as a principal residence, there may be a future capital gain payable upon its sale or disposition. Or, if the child is married/common-law, what happens if there is a marital breakdown? We recommend seeking the advice of tax and family law professionals.
These are just two of the challenges that may impact retirement planning. For a deeper discussion, please get in touch.
[1] www.theglobeandmail.com/investing/personal-finance/article-parents-gave-their-adult-kidsmore-
than-10-billion-to-buy-houses-in/; [2] www.theglobeandmail.com/investing/personal-finance/
young-money/article-nine-in-10-parents-are-helping-their-adult-kids-financially-heres-how/
The $10-Billion Bank of Mom and Dad
$10 Billion: According to one estimate, that’s how much parents gave kids in 2021 to fund a down payment on a home.1 Back in 2015, the average gift was $52,000; in 2021, it was closer to $82,000, an increase on average of 9.7 percent per year.1 One personal finance expert suggested we may be at a “tipping point for parental obligation.” Is this the new normal, where parents now plan for this expense alongside their own retirement?
BEHAVIOURAL FINANCE & INVESTING
Take a Vacation from Checking Your Portfolio
An article in the Washington Post offered a different perspective to the view that kids these days get too much screen time. There’s another demographic struggling to put down their devices: baby boomers. As one man put it: “My 75-year-old dad’s phone may as well be an implant; he lives with it like a teenager!”1 Of course, this has implications for our investing ways. With easy access at our fingertips, we may all be guilty of checking investment accounts too frequently. This summer, why not take a vacation from checking your portfolio? Here are some reasons why:
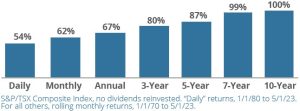
The more you check, the greater likelihood of seeing negative performance. History has shown that by checking the stock market daily, the chances of seeing a negative return are 46 percent. However, this reduces to 0 percent for 10-year rolling monthly returns. As the graph (right) reminds us, the longer you extend your time horizon, the better the chances of seeing positive returns.
Emotions can impact our investing decisions. Behavioural finance suggests that we feel losses twice as acutely as we feel gains of a similar size. “Myopic loss aversion” can occur when we react too hastily to avoid these losses, often making decisions that are not in our longer-term best interests. One important variable for investing success is how long you can stay invested. As Warren Buffett’s business partner Charlie Munger often says: “The big money is not in the buying or selling, but in the waiting.”
Investing often involves patience. When the S&P 500 Index hit a level of 4,200 in May (rising 20 percent from its October trough), some market pundits asked: Is this the start of a new bull market? While the S&P/TSX Composite hasn’t officially entered a bear market, the S&P 500 has been in a bear market since last year. Over the past 50 years, there have been six S&P 500 bear markets that lasted on average 15 months from peak to trough. In order to regain those losses, it took an average of 30 additional months.2 After the last bear market — the shortest ever at a mere 33 days during the pandemic — we may have been conditioned to believe the markets quickly rebound. Yet, enduring bear markets can often take time. The good news? Markets are cyclical: history reminds us that they’ve always recovered to reach new highs.
[1] www.washingtonpost.com/technology/2022/11/12/boomers-screentime/; [2] Based on: awealthofcommonsense.com/2023/03/why-the-stock-market-makes-you-feel-bad-all-the-time/
Chart: How Often is the S&P/TSX Composite Positive?
A POTENTIAL INTERGENERATIONAL WEALTH TRANSFER TOOL
FHSA: Opportunities for High-Net-Worth Investors

The First Home Savings Account (FHSA) is a registered account that offers significant tax-savings and growth opportunities, intended for the purchase of a first home. Eligible Canadian residents ages 18 or older who are first-time home buyers can contribute up to $8,000 per year, to a lifetime maximum of $40,000. Contributions are tax deductible, similar to the Registered Retirement Savings Plan (RRSP), and withdrawals are tax free, similar to the Tax-Free Savings Account (TFSA), if used to purchase a first home. The FHSA can generally stay open for 15 years (or until the year after the first qualifying withdrawal or the holder reaches age 71).
Beyond the opportunity to support those purchasing a first home, the FHSA may provide opportunities for high-net-worth (HNW) investors:
- It may act as a significant intergenerational wealth transfer tool;
- For those who haven’t owned a home in the past four years, it may provide a tax-advantaged way to supplement retirement savings.
Many parents and grandparents gift funds to younger folks to help cover large expenses such as an education or first home purchase. Some HNW investors support a child’s education through the Registered Education Savings Plan but often stop contributions once the Canada Education Savings Grants cease. The opportunity to then gift funds to a child to contribute to their FHSA starting at age 18 may be a great way to transfer wealth to the next generation, keeping in mind the loss of control with gifted funds. If the FHSA is opened at age 18, it must be closed in the calendar year after turning age 33. By some accounts, this is the average age of a first-time home buyer.1
For HNW renters, the FHSA may also provide an opportunity for tax-deductible contributions and tax-deferred growth. The account would need to be closed by age 71 if the 15-year limit isn’t reached, but the holder could transfer amounts to an RRSP/RRIF without affecting existing contribution room.
Since the FHSA can generally remain open for a maximum of 15 years, here are three tips to potentially maximize the growth opportunity.
1. Start early. Since the FHSA must be closed in the year after making the first qualifying withdrawal, if the holder intends to purchase a first home, the account’s life may be shortened. Opening the account
as early as possible may allow for compounded growth over the longest period possible.
2. Maximize contributions from the outset. Making full contributions at the start of each year can maximize the growth potential. Unused portions of the annual limit carry forward, but the carry-forward is limited to a maximum of $8,000 in the following year.
3. Consider the way that funds are invested. Given the substantial tax-advantaged opportunity to grow funds, consider investing in quality securities that provide meaningful growth and return potential.
By maximizing contributions from the outset, the account could grow to over $75,000 in 15 years, assuming a compounded annual rate of return of 5 percent, and this doesn’t include the tax benefit from initial contributions. Alongside the Home Buyers’ Plan under the RRSP, a couple who are both first-time buyers could fund a substantial downpayment. If the holder decides not to purchase a home, the FHSA can be transferred to an RRSP/RRIF without affecting the available contribution room.
Consider also that, generally, contribution amounts not claimed as a deduction on an income tax return in the year made can be claimed in a future year — even beyond the FHSA’s closure. This may provide a substantial tax benefit if saved for future years when the holder’s marginal tax rate may be significantly higher.
To learn more about the FHSA’s potential benefits, please call the office. [1] cdn.nar.realtor/sites/default/files/documents/2021-highlights-from-the-profile-of-home-buyers-and-sellers-11-11-2021.pdf
KEEP YOUR ASSETS WORKING HARD
Billions and Trillions: Unclaimed or Available
It’s the summertime, a time when many of us prefer to be idle. If you are pursuing more relaxing endeavours, make sure your assets keep working hard for you. In brief, here are three considerations:
1. Have you fully maximized tax-advantaged accounts? By now, you have likely received your Notice of Assessment from the Canada Revenue Agency (CRA) for your 2022 taxes. Do you have available RRSP or TFSA contribution room? The latest statistics suggest there is over $1 trillion of unused RRSP contribution room available.1 Similarly, most TFSA holders have not maximized their contribution room.2
2. Do you have unclaimed assets? The number of unclaimed
or forgotten assets continues to grow, serving as a reminder of the benefits of consolidating financial accounts to prevent assets from becoming orphaned over time. The latest reports suggest that $1.1 billion of unclaimed balances are held by the Bank of Canada. The CRA has 8.9 million uncashed cheques equating to over $1.4 billion. Does any belong to you? To search for unclaimed assets, see: www.unclaimedproperties.bankofcanada.ca/app/claim-search. Check your CRA “My Account” for unclaimed cheques at: www.canada.ca/en/revenue-agency/services/uncashed-cheque.htmlactive.
3. Are you keeping in good standing with the CRA? Consider that the CRA’s prescribed rate, which is adjusted quarterly based on prevailing interest rates, currently stands at 5 percent.3 More prominently, the interest charged on insufficient or late instalments, other remittances and penalties, has risen to nine percent! This may be particularly notable for investors who make quarterly instalment payments or remit payroll taxes for a small business: Be on time to avoid costly interest charges!
The CRA continues to crack down on tax mishandling. Recently, it held back tax refunds for those who incorrectly claimed pandemic benefits, recovering $237 million.4 It continues to monitor real
estate transactions to curb non-compliance for property sales and unreported capital gains, completing over 61,000 real estate audits. The Residential Property Flipping Rule that began this year is intended to
support the CRA in clarifying a taxpayer’s obligations, with profits from the sale of a property held for less than 365 days generally treated as business income.
[1] At 2016; Statistics Canada Table 111-0040 “RRSP Room”; [2] www.canada.ca/content/dam/cra-arc/prog-policy/stats/tfsa-celi/2019/table3-en.pdf; [3] www.canada.ca/en/revenue-agency/services/tax/prescribed-interest-rates.html; [4] www.cbc.ca/news/politics/cra-witholding-tax-refunds-pandemic-benefits-1.6829594
Macroeconomic Perspectives:
The Fed Pause: Are We Near the End of the Rate Cycle?

If talk of interest rate increases has seemed unending, you’re not mistaken: we are in one of the most aggressive tightening cycles in 40 years. In May, the U.S. Federal Reserve raised rates for the 10th consecutive time in its fight to bring down inflation.
In less than 14 months, the federal funds rate increased by a total of 5 percentage points (500 bps) to 5.25 percent from where it stood at 0.25 percent in March 2022. The Bank of Canada has similarly increased interest rates, raising the overnight rate by 0.25 percent to 4.75 percent at the start of June.
However, in its latest rate announcement in June, the Fed held rates steady for the first time since it began its tightening cycle, though it signaled that it may still be open to future hikes. This has prompted some to ask: Are we nearing the end of the rate cycle?
Until recently, the effects of the rapid rate hikes have appeared relatively benign. One market strategist suggested that if you were to tell investors two years ago that we would be entering one of the most aggressive rate increase cycles in history, alongside inflation that would reach 9 percent in the U.S. (and 8 percent in Canada), you would think that there would be greater effects on the stock market.1 For example, one way to value an investment is by using a discounted cash flow method which looks at future cash flows: a higher discount rate should make today’s present value of future cash flows lower. Yet, in May 2023, both the S&P 500 and the S&P/TSX Composite hovered around similar levels to those of May 2021.
Glass Half-Empty or Half-Full: Are We Headed to Recession?
The regional banking sector fallout in the U.S. this past spring was a reminder that there were likely to be follow-on effects from the unprecedented speed and magnitude of the hikes. After all, these actions were intended to slow the economy. As part of the normal course in every business cycle, some businesses will collapse, making room for others to grow. Yet, it is somewhat confounding that unemployment levels remain at lows and consumer spending has been relatively strong. Despite the expectation for slower growth, the latest earnings season has been positive. For many months, market pundits have suggested an imminent recession, but these factors may suggest otherwise.
Equity Markets: What Happens at the End of the Rate Cycle?
If we are nearing the end of the cycle, if history is any indicator, it may be good news for the equity markets. A look back at past tightening cycles shows that equity markets have historically performed well in the year after the final rate increase.2 Similarly, analyses show that the markets have rallied in the months after a pause.3
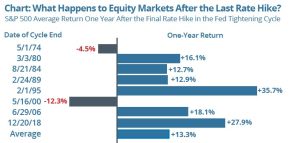
Source: Strategas; https://ritholtz.com/2023/05/10-thursday-am-reads-430/
However, in the near term, a resilient labour market and more sticky inflation, recently driven by service sector growth and the housing market, could contribute to keeping interest rates elevated — all of which are carefully being watched and likely to influence future rate decisions.
Of course, from our perspective as we manage assets for the long term, the challenge for investors is ignoring the day-to-day noise and continuing to position assets for when we will eventually need to access our capital — sometimes a decade or two into the future, or more, depending on your timeline. For many investors, longer-term returns are the only ones that matter. Though we may all appreciate some respite from the volatility of the past two years, consider also that buying when prices are lower is one of the best ways to improve longer-term results. Keep perspective and continue looking forward.
[1] awealthofcommonsense.com/2023/05/how-interest-rates-inflation-impact-stock-market-valuations/; For historical rate hike cycles, please refer to: https://www.cnbc.com/2015/09/15/when-the-fed-raises-rates-heres-what-happens.html; [2] ritholtz.com/2023/05/10-thursday-am-reads-430/; [3] ritholtz.com/2023/05/10-wednesday-am-reads-330/; bloomberg.com/news/articles/2023-05-06/wall-street-is-in-no-mood-to-celebrate-the-fed-s-last-rate-hike
