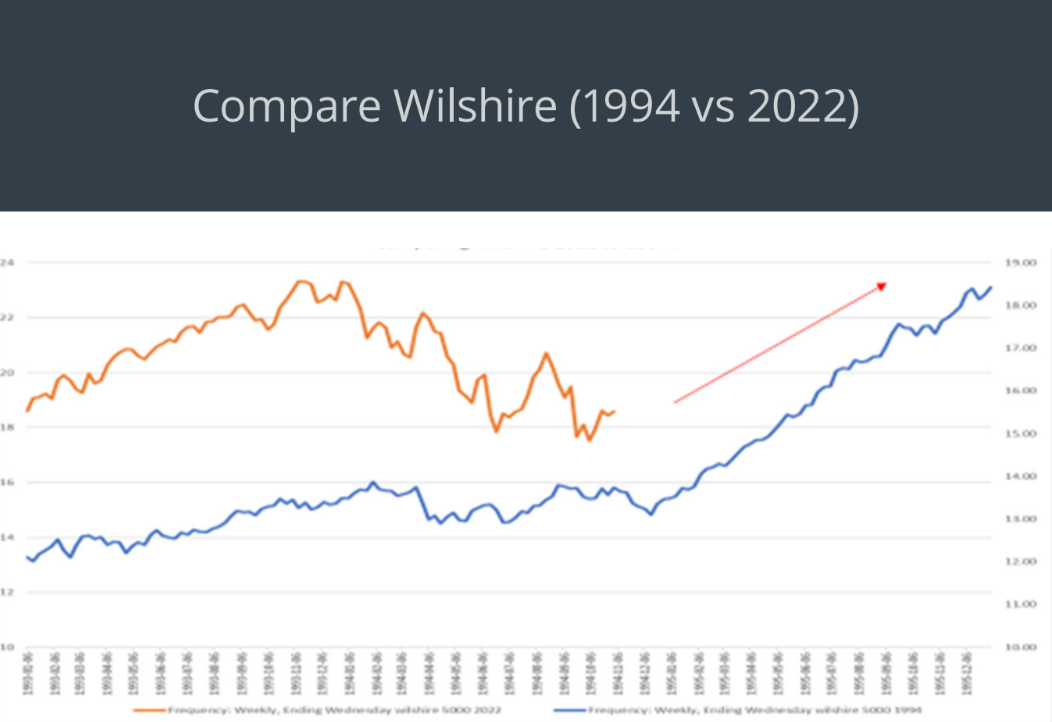
After the 1994 midterm elections, gridlock was confirmed and inflation fears subsided. The next year, the Fed cut rates, and risk assets appreciated. The recent Consumer Price Index (CPI) data points to 2023 reversing the inflation shock, interest rate shock, and growing fears of 2022. The Bull narrative for 2023 will be: inflation has peaked, rate hikes have peaked, the U.S. dollar has peaked, and yields have peaked. Recent market action suggests capital markets are already starting to discount the new narrative.
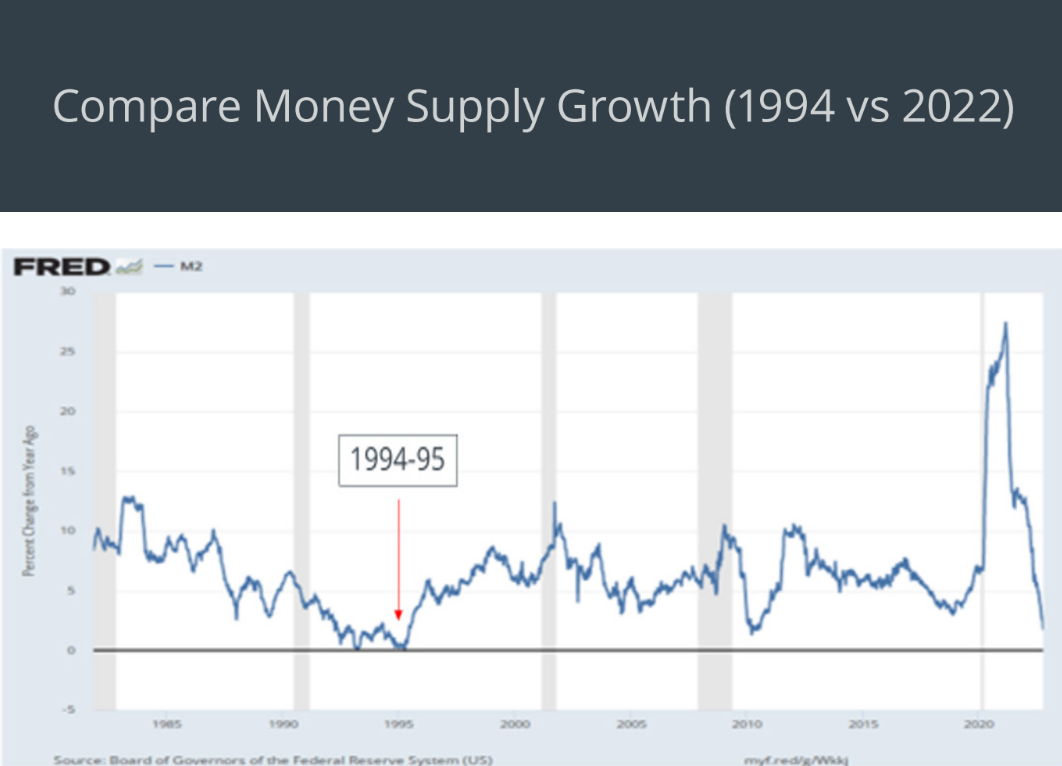
In the post-WWII era, debt levels were close to the levels seen today, populism was strong, and the U.S. experienced three years of average inflation of over 10 per cent. In this era, inflation was beaten by not aggressively raising rates; but by letting the supply shocks that caused the inflation to work out. The period starting in 1994, saw the Fed aggressively raise rates in a mid-term election year. The concern was that the policies put forth by the new Clinton administration were going to lead to permanent inflation. Once the Republicans, led by Mr. Gingrich, won the mid-term election, the ensuring gridlock led to inflationary pressures quickly receding, and resulted in the Fed cutting rates in 1995. Add the similarities in demographics; today, millennials are entering their prime family formation years; in the 1990’s it was the boomers.
The continued evolution from analog to digital keeps the job market tight. It allows the Fed to generate a soft landing. The preliminary results of the U.S. midterm elections point to the death of the Biden policy agenda just as was the case in the mid-1990s with President Clinton’s plan. The economy will continue to digest the twin supply shocks of Covid-19 and war. With gridlock now a reality in Washington, D.C., long-term and short-term inflationary concerns will continue to decline rapidly in 2023. To wit, inflationary breakeven suggests this to be the case, and investors have chosen to ignore the signals and anchor off the market’s noise. Some things never change.
In this politically charged environment, one of the midterm elections’ most interesting, yet not surprising, results was that the Red Wave, the big republican sweep, did not materialize. Yes, the Republicans will gain control of the House of Representatives and thus control the government’s purse strings, rendering the Biden agenda dead for all intents and purposes. But the hidden lead was the poor results by candidates with extreme political views. Mr. Trump and the candidates he supported were the actual losers in many of the competitive races. Independent voters are getting tired of the extreme policy platforms of both the left and the right. To be sure, the winner of the governor race in Virginia by a moderate Republican should have been the warning sign.
The Democrats incorrectly assumed that the Biden win was a referendum on their economic and social platform that independents accepted. It was a referendum on former President Trump. Donald Trump’s announcement of his candidacy for the 2024 presidential elections infers that many still believe that extreme policies can win elections. The results of the recent mid-term elections suggest otherwise.
In 1929, Harold Hotelling suggested that in a majority-rule voting system, the candidate or party most preferred by the median voter will win the election. We know this theory today as Hotelling’s Law.
In other words, political parties’ platforms should migrate to the center over time. But in this age of populism, this has not been the reality. That said, look at the early results; moderate candidates in both the Republican and the Democratic parties performed surprisingly well. Why should investors care? Gridlock in Washington D.C. and moderate policies are good for markets. With the demographic baton being passed from the boomer generation to the millennials, what society deems middle ground is sure to change as history teaches us. However, focusing on debt, budget deficits, and policies that help the economy evolve in an environment of low inflation set the stage for a much less restrictive monetary policy in the future. History suggests when monetary and fiscal policy are aligned, risk assets benefit.
WHY SHOULD INVESTORS CARE?